Unlike embryonic stem cells there are many different types of adult stem cells, found in numerous different parts of the body. They are undifferentiated cells surrounded by differentiated cells such as a tissue or organ. Additionally called somatic stem cells, their main jobs are to "maintain and repair the tissues in which they are found." (5)
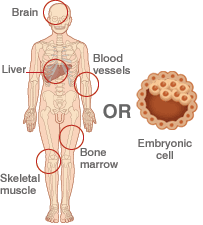
Adult stem cells are becoming increasingly popular to experiment with because it does not hold the controversy issues that embryonic stem cells do and have a much lower chance of causing the patient to experience immune rejection to the treatment. Immune rejection could cause some very serious problems, and in some cases even death has occured. "Adult stem cells have been identified in many organs and tissues, including brain, bone marrow, peripheral blood, blood vessels, skeletal muscle, skin, teeth, heart, gut, liver, ovarian epithelium, and testis." (6)
Adult Stem Cells
4.

7.
Collecting adult stem cells
There are multiple different methods when extracting adult stem cells from a body. One of them is the peripheral blood stem cell harvest procedure. During this procedure large quantities of chemotherapy would be given to the patient killing large doses of their white blood cells. The lack of white blood cells causes the bone marrow to franticly work to replace it. Shortages of room for all of the new stem cells inside of the bone marrow forces them into the blood stream to differentiate more quickly. With a combination of two different drugs, the amount of stem cells circulating through the blood stream reaches it's peak.
Approximently seven days after these procedures patients will return for the extraction of their stem cells. The patients would either be sitting or lying down with an IV going through both of their arms. The pheresis machine proceeds to isolate the stem cells and return the blood to the patient. (18)

One example of these are hematopoietic stem cells which are found in bone marrow after birth, that helps regulate the production of blood cells. (6)
12.